ZeroShotCeres: Zero-Shot Relation Extraction from Semi-Structured Webpages (link)
-
In this work, the authors propose a solution for “zero-shot” open-domain relation extraction from webpages with a previously unseen template, including from new websites and new subject verticals.
-
ZEROSHOTCERES is a graph neural network model that encodes semantic textual and visual patterns common across different training websites.
-
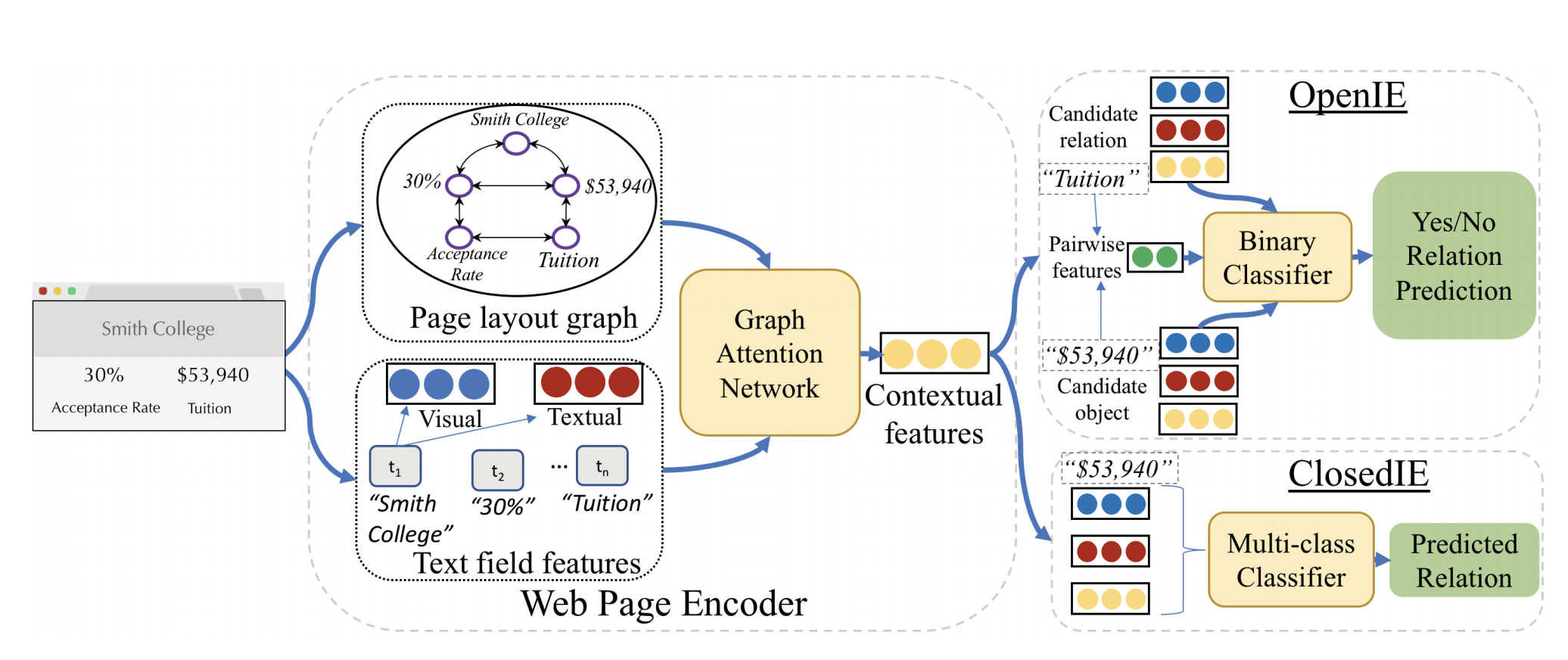
-
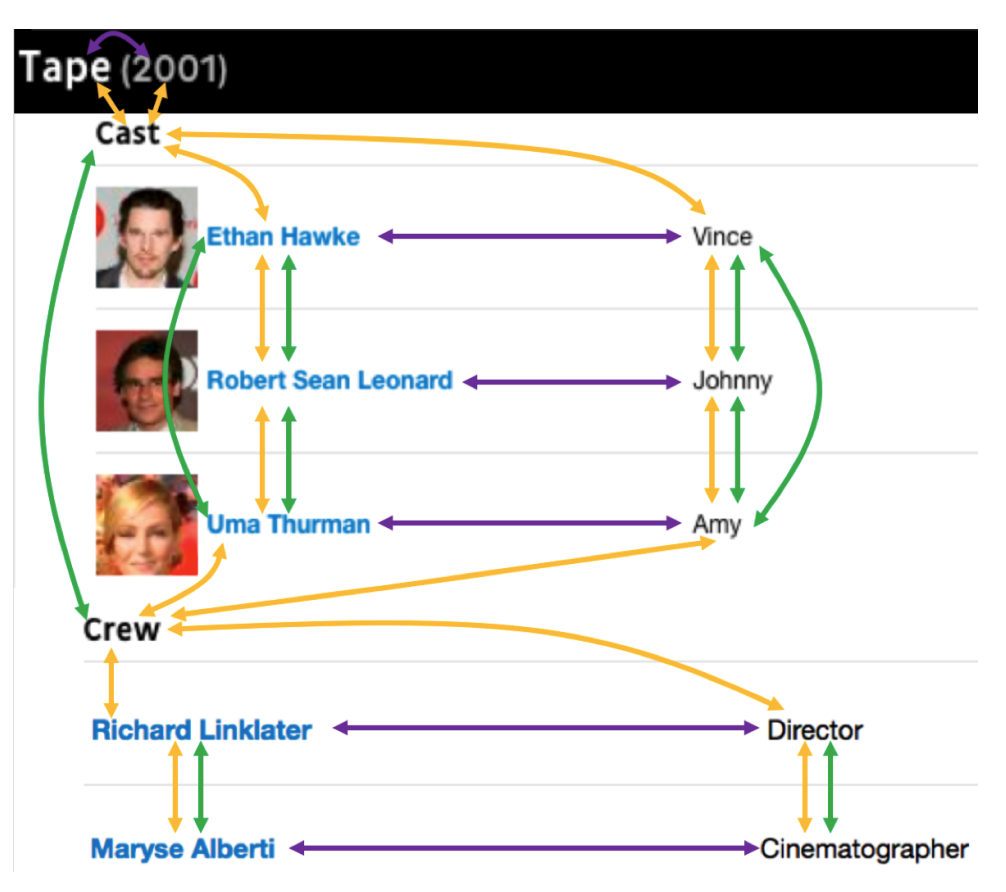
The method builds a graph to capture the layout relationships in a more abstract form to more easily learn the common features across different sites such as the fact that relation strings are often to the left or above their objects.
-
The method applies a Graph Neural Network (GNN) to learn representations for each node capturing contextual information about its neighborhood on the webpage, allowing information to flow through the nodes.
-
In the graph, the edges capture three forms of adjacency:
(1) Horizontal: Edges are added when two text fields are horizontal neighbors on the page;
(2) Vertical: Edges are added when two text fields are vertical neighbors on the page;
(3) DOM: Edges are added when two text fields are siblings or cousins in the DOM tree.
-
For each text field on the page, the authors produce an initial feature vector containing both visual feature vector V (bounding box coordinate, height and width, …) and **textual feature vector T **(texts processed with a pre-trained BERT, the percent of pages on the site on which the string in the text field appear).
-
The authors use a pre-training step to learn the GNN representation before incorporating it into the extraction mode and freeze the GNN weights during the full OpenIE training.
-
Extended SWDE dataset contains gold labels for 21 English language websites (each with one template) in three subject verticals (Movie, NBA, and University), with between 400 and 2,000 pages per site.
-
-
Comments:
- The setting of Closed IE is similar to Attribute Extraction in FreeDOM (KDD20).
- Dataset
- Pretraining enhances the generality.
- One suprising thing in the OpenIE setting: only a single textual feature is used (the percent of pages on the site on which the string in the text field appear).
Improving Low-Resource Named Entity Recognition using Joint Sentence and Token Labeling (link)
- L(sentence classification) acts as a regularization term which helps in avoiding overfitting.
- Sharing representations between two tasks leads to better generalization.
- Pretraining the parameters solely with the sentence classification task to initialize the joint training works better.
- The attention scaling factor is learned.
Probing Linguistic Features of Sentence-Level Representations in Relation Extraction (link)
- The complexity of the task makes it difficult to understand how encoder architecture and supporting linguistic knowledge affect the features learned by the encoder.
- Probing tasks (Shi et al., 2016; Adi et al., 2017), or diagnostic classifiers, are a well established method to analyze the presence of specific information in a model’s latent representations.
- Self-Attention encodes “deeper” linguistic information into the sentence representation, not covered by the current set of probing tasks.
- All proper encoders exhibit consistently high performance on TypeHead and TypeTail, while entence length is mostly irrelevant for RE.
- A severe overfitting to specific entity mentions exists when no entity masking is applied.
- Encoders that perform better on probing tasks do not necessarily perform better on the downstream RE task.
